Ant Robot
Objectives
Let's get familiar with how the AntBot work!
The primary objective of this project is to explore the use of infrared sensors, a.k.a. "IR sensors", in robotics. By building an ant-inspired robot, we will learn how these sensors mimic the navigation technique of ants to help the robot go around its environment.
Through this project, we will:
- Understand the working principles of infrared sensors.
- Gain hands-on experience in assembling and programming a simple robot.
- Learn about basic electronics and Arduino programming.
- Explore how sensors can be used for navigation and obstacle avoidance.
Requirements
Hardware
- Simple Robot Chassis Kit: Includes 2 DC motors, 2 wheels, and a battery holder.
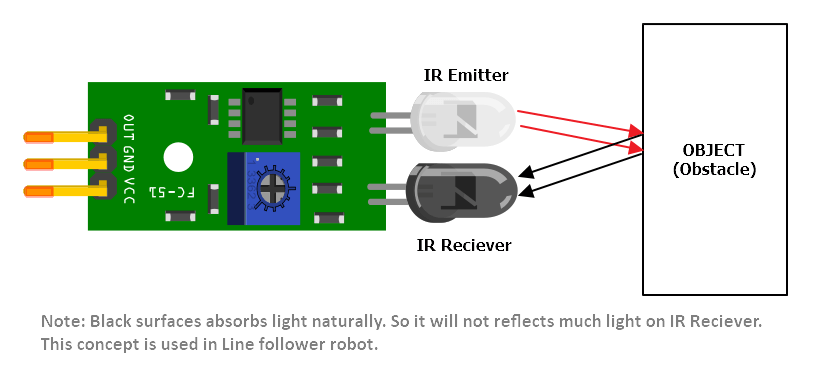
- Infrared Sensors: Sensors that change resistance when exposed to different light wavelengths.
- Arduino Uno + Cable: Microcontroller board for programming and controlling the robot.
- CAROBOT Motor Shield v3: Extension board for driving the motors.
- 0.1 microF Capacitors: For filtering noise in the circuit.
- Resistors:
- 220 ohm resistors for current limiting.
- 10k ohm resistor for the push button.
- Push Button: For starting or resetting the robot.
- Mini Breadboard: For creating the circuit connections.
- Jumper Wires: For connecting components on the breadboard.
- AA Batteries (x4): Power source for the robot.
Software
- Arduino IDE: Integrated Development Environment for writing and uploading code to the Arduino board.
- Basic C/C++ Programming Knowledge: To understand and write the Arduino code.
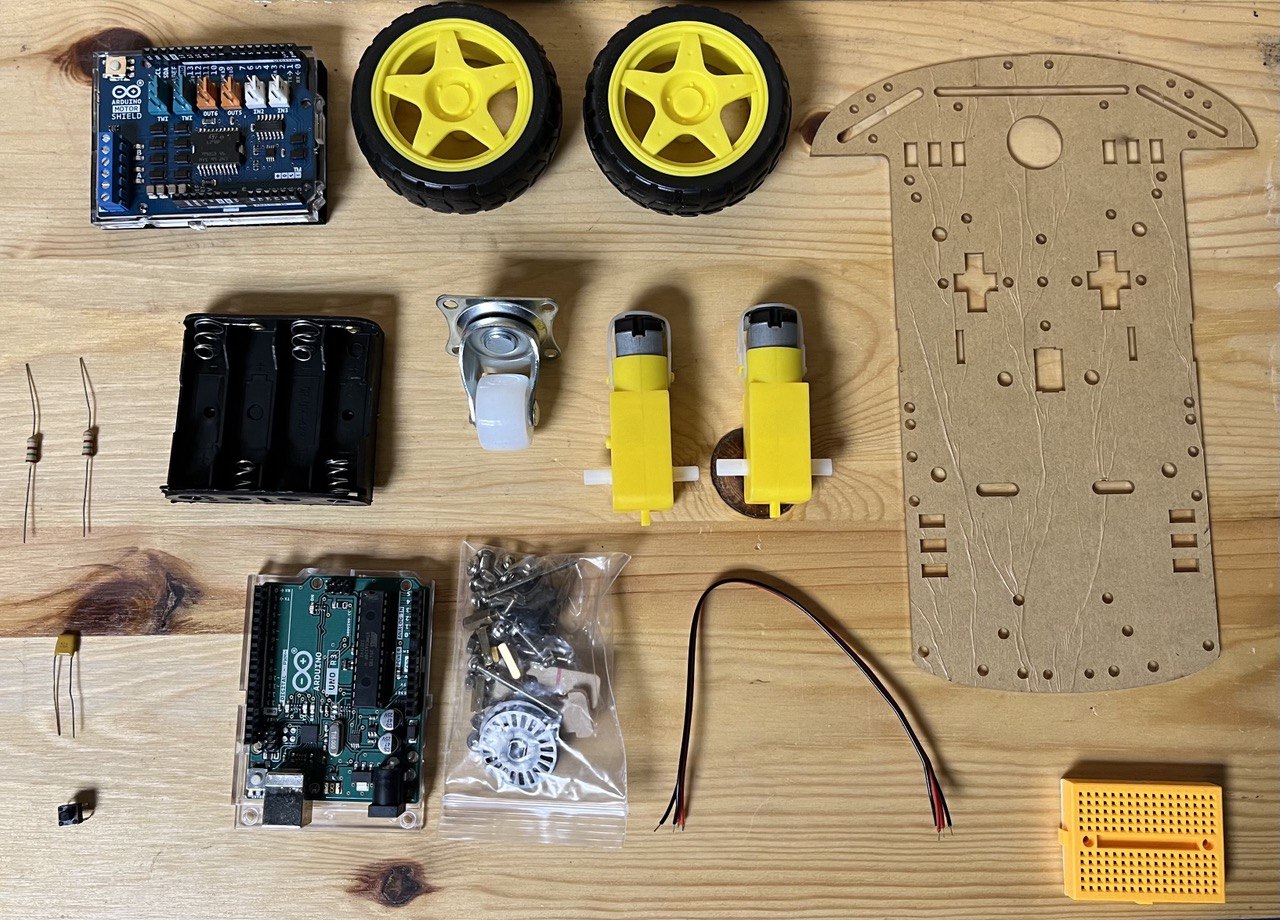
Bill of Material:
- Simple Robot Chassis Kit (2 DC motors, 2 Wheels, battery holder)
- IR sensor
- Arduino Uno + Cable
- CAROBOT motor shield v3
- 0.1 microF capacitor
- Generic resistor
- 10k Ohm resistor
- push button
- mini breadboard
- Jumper wires
- AA batteries
Design
The Beetle Robot is designed to mimic the behavior of an ant using its eyes for navigation. The design includes:
- Chassis and Motors: The base structure of the robot with wheels driven by DC motors.
- IR Sensors: Attached to the front of the robot, acting as eyes to detect light waves.
- Arduino and Motor Shield: Central control system that processes sensor data and controls the motors.
- Power Supply: Batteries to power the entire system.
- Push Button: For user interaction to start or reset the robot.
When the IR sensors detect the light path, they change their readings. The Arduino reads this change and makes the robot back away and change direction, simulating the ant’s behavior.
Implementation
- Assemble the Chassis: Attach the DC motors and wheels to the chassis. Insert the batteries into the holder.
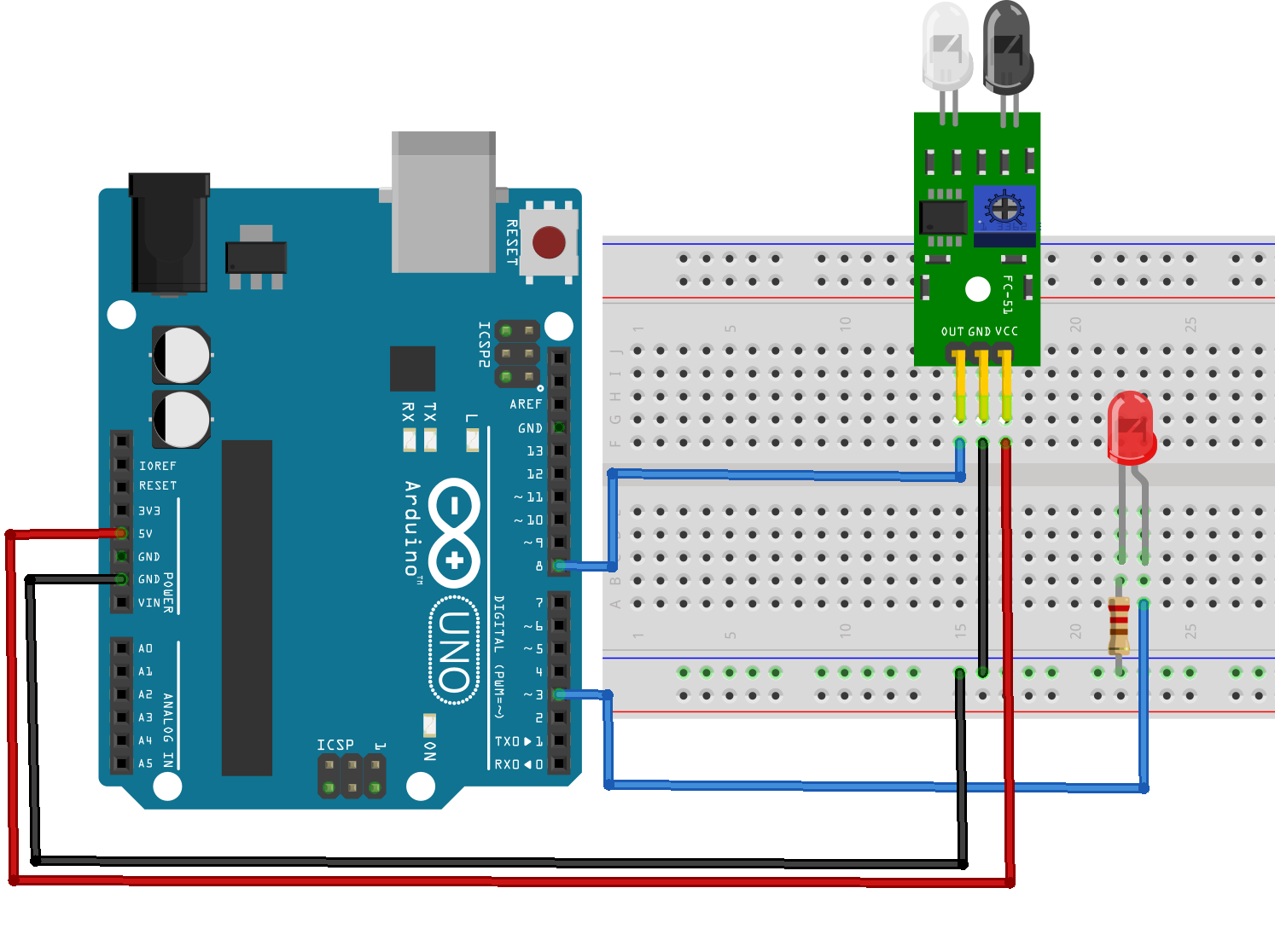
- Set Up the IR Sensors: Connect the IR sensors to the mini breadboard and wire them to the Arduino. Use the capacitors and resistors as needed.
- Install the Motor Shield: Attach the motor shield to the Arduino and connect the DC motors.
- Connect the Push Button: Wire the push button to the Arduino through the breadboard.
- Write the Code: Use the Arduino IDE to write a program that reads the infrared sensor data and controls the motors based on the sensor input.
- Test and Debug: Upload the code to the Arduino, test the robot’s functionality, and make necessary adjustments.
Conclusion
Through this project, you will have gained practical experience in building and programming a robot, understanding the use of IR sensors for navigation, and learning basic principles of electronics and robotics. This hands-on project not only enhances your technical skills but also emphasizes the "hows" and "whys" by demonstrating real-world applications of sensors and robotics.